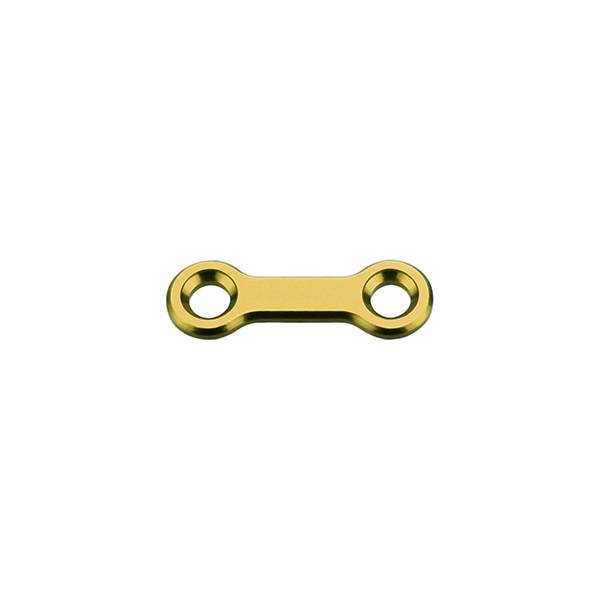
Material: medical pure titanium
Product specification
|
Thickness |
Length |
Item No. |
Specification |
|
0.4mm |
15mm |
00.01.03.02111515 |
Non-anodized |
|
00.01.03.02011515 |
Anodized |
|
Thickness |
Length |
Item No. |
Specification |
|
0.4mm |
17mm |
00.01.03.02111517 |
Non-anodized |
|
00.01.03.02011517 |
Anodized |
|
Thickness |
Length |
Item No. |
Specification |
|
0.6mm |
15mm |
10.01.03.02011315 |
Non-anodized |
|
00.01.03.02011215 |
Anodized |
|
Thickness |
Length |
Item No. |
Specification |
|
0.6mm |
17mm |
10.01.03.02011317 |
Non-anodized |
|
00.01.03.02011217 |
Anodized |
Features & Benefits:
• No iron atom, no magnetization in magnetic field. No effect to ×-ray, CT and MRI after operation.
• Stable chemical properties, excellent biocompatibility and corrosion resistance.
• Light and high hardness. Sustained protect brain issue.
• Fibroblast can grow into the mesh holes after operation, to make the titanium mesh and tissue integrated. Ideal intracranial repair material!
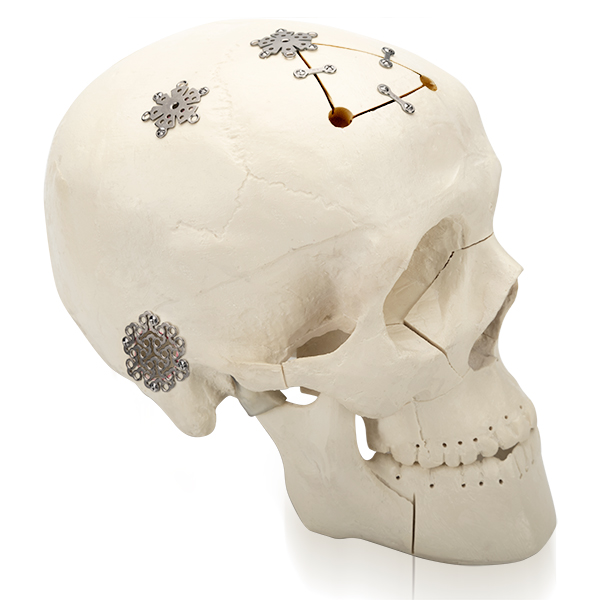
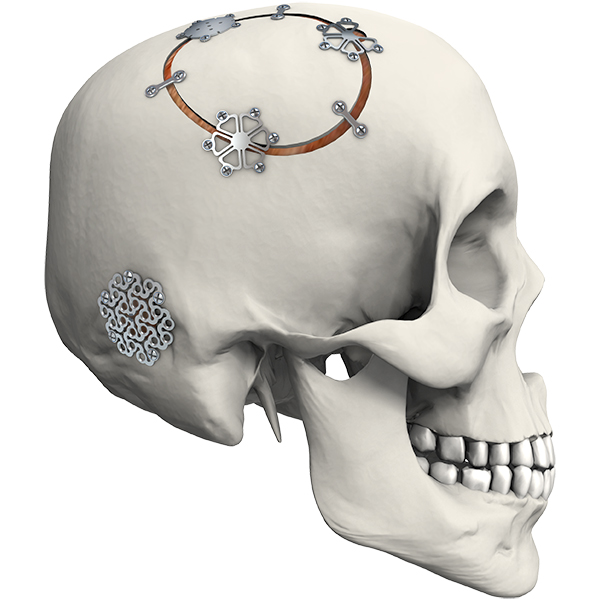
Matching screw:
φ1.5mm self-drilling screw
φ2.0mm self-drilling screw
Matching instrument:
cross head screw driver: SW0.5*2.8*75mm
straight quick coupling handle
cable cutter (mesh scissors)
mesh moulding pliers
Two holes straight plate is a streamlined, comprehensive system that offers flexibility, ease of use, and high-quality implants and instruments. Low plate-screw profile of 0.5 mm for minimal implant palpability. Single instrument system for rapid and stable fixation of cranial bone flaps.
Skull is a bony structure that forms the head in vertebrates. Skull bones support the structures of the face and provides a protective cavity. Skull is made up of two parts: cranium and the mandible. These two parts of humans are the neurocranium and the facial skeleton that includes the mandible as its largest bone. Skull protect brain, fix the two eyes’ distance, fix the positon of the ears to enable sound localisation of the direction and distance of sounds. usually occurring as a result of blunt force trauma, skull fracture may be a break in one or some of the eight bones that form the cranial portion of the skull.
Fracture may happen at or near the site of the impact and damage to the underlying structures within the skull such as the membranes, blood vessels, and brain. skull fractures have four major types, linear, depressed, diastatic, and basilar. The most common type is linear fractures, but no need to perform medical intervention.Usually, depressed fractures are usually comminuted with many inward broken bones displaced, so need surgical intervention to repair underlying tissue damage. Diastatic fractures widen the sutures of the skull affect children that age under three.Basilar fractures are in the bones at the base of the skull.
Depressed skull fracture. Get struck with a hammer, rock or getting kicked in the head and other types of blunt force trauma usually result in a depressed skull fracture. 11% of severe head injuries occure in these types of fractures are comminuted fractures in which broken bones displace inward. Depressed skull fractures present a high risk of increased pressure on the brain, or a hemorrhage to the brain that crushes the delicate tissue.
When there is a laceration over the fracture, Compound depressed skull fractures will happen. putting the internal cranial cavity in contact with the outside environment, increasing the risk of contamination and infection. In complex depressed fractures, the dura mater is torn. Surgery must been performed for depressed skull fractures to lift the bones off the brain if they are pressing on it by making burr holes on the adjacent normal skull.
Human skull is anatomically divided into two parts: the neurocranium, formed by eight cranial bones that houses and protect the brain, and the facial skeleton (viscerocranium) composed of fourteen bones, not including the three ossicles of the inner ear. Skull fracture typically means fractures to the neurocranium, while fractures of the facial portion of the skull are facial fractures, or if the jaw is fractured, a mandibular fracture.
Eight cranial bones are separated by sutures : one frontal bone, two parietal bones, two temporal bones, one occipital bone, one sphenoid bone, and one ethmoid bone.
-
maxillofacial trauma mini double Y plate
-
locking maxillofacial mini straight bridge plate
-
maxillofacial trauma micro straight plate
-
orthognathic anatomical 1.0 L plate
-
orthognathic 0.8 genioplasty plate
-
maxillofacial trauma micro 110° L plate