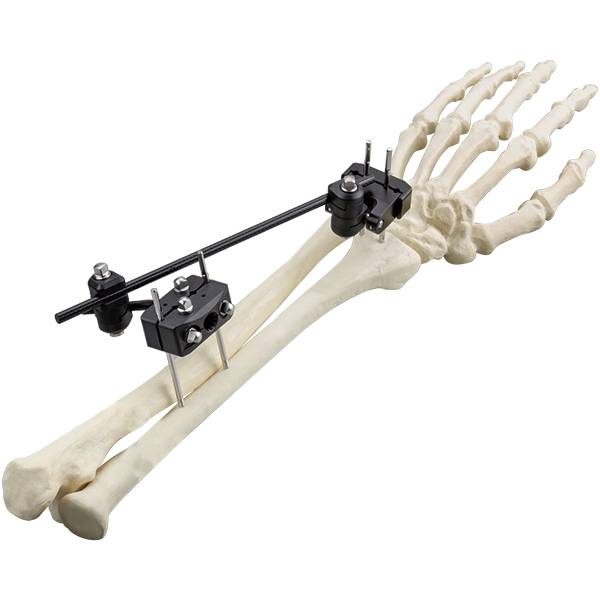
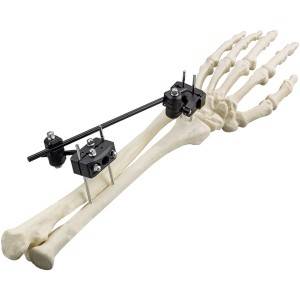
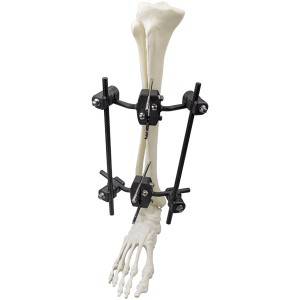
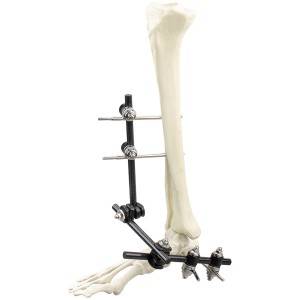
Features:
1. Thread guidance locking mechanism prevents the occurrence of screw withdrawal.
2. Low profile design helps reduce soft tissue irritation.
3. The locking plate is made of Grade 3 medical titanium.
4. The matching screws are made of Grade 5 medical titanium.
5. Afford MRI and CT scan.
6. Surface anodized.
7. Various specifications are available.
Specification:
Prosthesis and revision femur locking plate

|
Item No. |
Specification (mm) |
|
|
10.06.22.02003000 |
2 Holes |
125mm |
|
10.06.22.11103000 |
11 Holes, Left |
270mm |
|
10.06.22.11203000 |
11 Holes, Right |
270mm |
|
10.06.22.15103000 |
15 Holes, Left |
338mm |
|
10.06.22.15203000 |
15 Holes, Right |
338mm |
|
10.06.22.17103000 |
17 Holes, Left |
372mm |
|
10.06.22.17203000 |
17 Holes, Right |
372mm |
Φ5.0mm locking screw (Torx drive)

|
Item No. |
Specification (mm) |
|
10.06.0350.010113 |
Φ5.0*10mm |
|
10.06.0350.012113 |
Φ5.0*12mm |
|
10.06.0350.014113 |
Φ5.0*14mm |
|
10.06.0350.016113 |
Φ5.0*16mm |
|
10.06.0350.018113 |
Φ5.0*18mm |
|
10.06.0350.020113 |
Φ5.0*20mm |
|
10.06.0350.022113 |
Φ5.0*22mm |
|
10.06.0350.024113 |
Φ5.0*24mm |
|
10.06.0350.026113 |
Φ5.0*26mm |
|
10.06.0350.028113 |
Φ5.0*28mm |
|
10.06.0350.030113 |
Φ5.0*30mm |
|
10.06.0350.032113 |
Φ5.0*32mm |
|
10.06.0350.034113 |
Φ5.0*34mm |
|
10.06.0350.036113 |
Φ5.0*36mm |
|
10.06.0350.038113 |
Φ5.0*38mm |
|
10.06.0350.040113 |
Φ5.0*40mm |
|
10.06.0350.042113 |
Φ5.0*42mm |
|
10.06.0350.044113 |
Φ5.0*44mm |
|
10.06.0350.046113 |
Φ5.0*46mm |
|
10.06.0350.048113 |
Φ5.0*48mm |
|
10.06.0350.050113 |
Φ5.0*50mm |
|
10.06.0350.055113 |
Φ5.0*55mm |
|
10.06.0350.060113 |
Φ5.0*60mm |
|
10.06.0350.065113 |
Φ5.0*65mm |
|
10.06.0350.070113 |
Φ5.0*70mm |
|
10.06.0350.075113 |
Φ5.0*75mm |
|
10.06.0350.080113 |
Φ5.0*80mm |
|
10.06.0350.085113 |
Φ5.0*85mm |
|
10.06.0350.090113 |
Φ5.0*90mm |
|
10.06.0350.095113 |
Φ5.0*95mm |
|
10.06.0350.100113 |
Φ5.0*100mm |
Φ4.5 cortex screw (Hexagon drive)

|
Item No. |
Specification (mm) |
|
11.12.0345.020113 |
Φ4.5*20mm |
|
11.12.0345.022113 |
Φ4.5*22mm |
|
11.12.0345.024113 |
Φ4.5*24mm |
|
11.12.0345.026113 |
Φ4.5*26mm |
|
11.12.0345.028113 |
Φ4.5*28mm |
|
11.12.0345.030113 |
Φ4.5*30mm |
|
11.12.0345.032113 |
Φ4.5*32mm |
|
11.12.0345.034113 |
Φ4.5*34mm |
|
11.12.0345.036113 |
Φ4.5*36mm |
|
11.12.0345.038113 |
Φ4.5*38mm |
|
11.12.0345.040113 |
Φ4.5*40mm |
|
11.12.0345.042113 |
Φ4.5*42mm |
|
11.12.0345.044113 |
Φ4.5*44mm |
|
11.12.0345.046113 |
Φ4.5*46mm |
|
11.12.0345.048113 |
Φ4.5*48mm |
|
11.12.0345.050113 |
Φ4.5*50mm |
|
11.12.0345.052113 |
Φ4.5*52mm |
|
11.12.0345.054113 |
Φ4.5*54mm |
|
11.12.0345.056113 |
Φ4.5*56mm |
|
11.12.0345.058113 |
Φ4.5*58mm |
|
11.12.0345.060113 |
Φ4.5*60mm |
|
11.12.0345.065113 |
Φ4.5*65mm |
|
11.12.0345.070113 |
Φ4.5*70mm |
|
11.12.0345.075113 |
Φ4.5*75mm |
|
11.12.0345.080113 |
Φ4.5*80mm |
|
11.12.0345.085113 |
Φ4.5*85mm |
|
11.12.0345.090113 |
Φ4.5*90mm |
|
11.12.0345.095113 |
Φ4.5*95mm |
|
11.12.0345.100113 |
Φ4.5*100mm |
|
11.12.0345.105113 |
Φ4.5*105mm |
|
11.12.0345.110113 |
Φ4.5*110mm |
|
11.12.0345.115113 |
Φ4.5*115mm |
|
11.12.0345.120113 |
Φ4.5*120mm |
Distal radius fractures (DRFs) occur within 3 cm of the distal part of the radius, which is the most common fracture in the upper limbs among older women and young adult males. Studies reported that DRFs accounts for 17% of all fractures and 75% of forearm fractures.
Satisfactory results cannot be obtained by manipulative reduction and plaster fixation. These fractures can easily shift in position after conservative management, and complications, such as traumatic bone joint and wrist joint instability, may occur in the late stage. Surgeries are performed to treat distal radius fractures so that patients can perform an adequate number of painless exercises to restore normal activity while minimizing the risk of degenerative change or disability .
The management of DRFs in patients aged 60 and over is performed using the following five common techniques: volar locking plate system, non-bridging external fixation, bridging external fixation, percutaneous Kirschner wire fixation, and plaster fixation.
Patients undergoing DRF surgery with open reduction and internal fixation have higher risk of wound infection and tendonitis .
External fixators are divided into the following two types: cross-joint and non-bridging. A cross-articular external fixator restricts the free movement of the wrist due to its own configuration. Nonbridging external fixators are widely used because they allow limited joint activity. Such devices can facilitate fracture reduction by fixing the fracture fragments directly; they allow easy management of soft tissue injuries and do not restrict natural wrist motion during the treatment period. Therefore, nonbridging external fixators have been widely recommend for DRF treatment. In the past few decades, the use of traditional external fixators (titanium alloys) has gained popularity, because of their excellent biocompatibility, high mechanical strength and corrosion resistance. However, the traditional external fixators that are made with metal or titanium may cause severe artifacts in computed tomography (CT) scans, which has led to researchers looking for new materials for external fixators.
Internal fixation based on polyetheretherketone (PEEK) has been studied and applied for more than 10 years. The PEEK device has the following advantages over materials used for traditional orthopedic fixation: no metal allergies, radiopacity, low interference with magnetic resonance imaging (MRI), easier implant removal, avoiding the “cold welding” phenomenon, and better mechanical properties. For example, it has good tensile strength, bending strength, and impact strength.
Some studies have shown that PEEK fixators have better strength, toughness, and stiffness than metal fixation devices, and they have better fatigue strength13. Although the elastic modulus of the PEEK material is 3.0–4.0 GPa, it can be strengthened by carbon fiber, and its elastic modulus can be close to that of cortical bone (18 GPa) or reach the value of titanium alloy (110 GPa) by changing the length and direction of the carbon fiber. Therefore, the mechanical properties of PEEK are close to those of bone. Nowadays, the PEEK-based external fixator has been designed and applied in clinic.
-
Φ8.0 Series External Fixation Fixator – T...
-
Φ8.0 Series External Fixation Fixator – F...
-
Φ11.0 Series External Fixation Fixator – ...
-
Φ5.0 Series External Fixation Fixator – C...
-
Φ11.0 Series External Fixation Fixator – ...
-
Φ8.0 Series External Fixation Fixator – H...