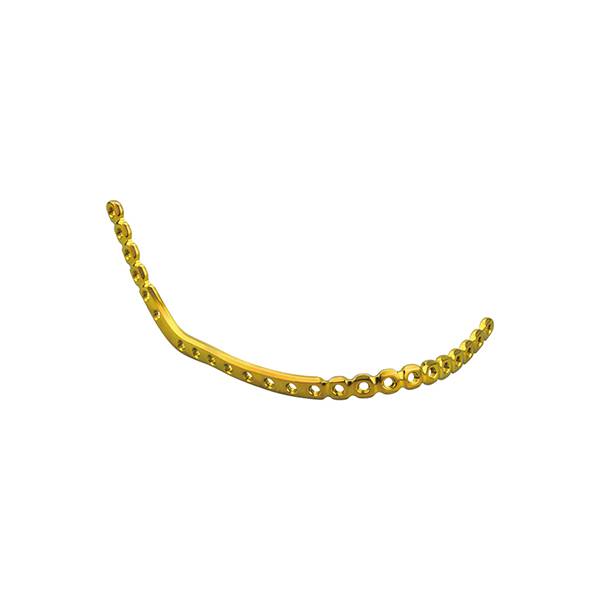
Material: medical pure titanium
Thickness: 2.4mm
Product specification
|
Item No. |
Specification |
|||
|
10.13.06.12117101 |
left |
S |
12 holes |
132mm |
|
10.13.06.12217101 |
right |
S |
12 holes |
132mm |
|
10.13.06.13117102 |
left |
M |
13 holes |
138mm |
|
10.13.06.13217102 |
right |
M |
13 holes |
138mm |
|
10.13.06.14117103 |
left |
L |
14 holes |
142mm |
|
10.13.06.14217103 |
right |
L |
14 holes |
142mm |
Indication:
• Mandible trauma:
Comminuted fracture of mandible, unstable fracture, infected nonunion and bone defect.
• Mandible reconstruction:
For first time or second reconstruction, used for bone graft or defect of dissociative bone blocks (If the first operation no bone graft, the reconstruction plate only ensure to bear a limited period of time, and must make a second bone graft operation to support the reconstruction pate).
Features & Benefits:
• pitch-row of reconstruction plate is a specalized design for fixation during operation, improve the stress concentration phenomenon in the specific area and fatigue strength.
• one hole select two kinds of screw: locking maxillofacial reconstruction anatomical plate can realize two fixed methods: locked and non-locked. Locking screw fixed bone block and at the same time firm lock the plate, like buill-in external fixation support. Non-locking screw can make an angle and compression fixation.
Matching screw:
φ2.4mm self-tapping screw
φ2.4mm locking screw
Matching instrument:
medical drill bit φ1.9*57*82mm
cross head screw driver: SW0.5*2.8*95mm
straight quick coupling handle
As an important facial organ to maintain beauty, the shape of the mandible plays an important role in facial aesthetics.Many factors such as trauma, infection, tumor resection and so on can cause the defect. The defect of the mandible not only affects the patient's appearance, but also causes abnormalities in chewing, swallowing, speech and other functions.The ideal mandibular reconstruction should not only achieve the continuity and integrity of the mandibular bone and restore the facial appearance, but also provide the basic conditions for the recovery of postoperative physiological functions such as chewing, swallowing and speech.
The cause of mandible defect
Tumor therapy: ameloblastoma, myxoma, carcinomas, sarcomas.
Avulsive traumatic injury: most commonly arise from high-velocity injuries such as firearms, industrial accidents, and occasionally motor vehicle collisions.
Inflammatory or infectious conditions.
Goals of Reconstruction
1. Restore the original shape of the lower third of the face and the mandible
2. Maintain the continuity of the mandible and restore the spatial position relationship between the mandible and the surrounding soft tissues
3. Restore good chewing, swallowing, and speech functions
4. Maintain adequate airway
There are four types of microreconstruction of mandibular defects.Trauma and tumor resection of the mandible may affect appearance and lead to functional deficits such as malocclusion due to unilateral muscle injury.In order to repair the appearance defect and reconstruct the function, many surgical methods have been developed, and the difficulty of the successful reconstruction of the mandible lies in the selection of the best method.Because of the complexity of mandibular defect, a set of simple, practical and generally accepted systematic classification and treatment methods is still blank.Schultz et al. demonstrated a new simplified classification method and the corresponding method for the reconstruction and repair of the mandible through practice, which was published in the latest journal of PRS.This classification focuses on vascular integrity in the recipient area, with a view to accurately repairing complex mandibular defects by microsurgical means.The method is first divided into four types according to the complexity of reconstructive surgery.The lower midline of the mandible was the boundary. Type 1 had a unilateral defect that did not involve the mandibular Angle, type 2 had a unilateral defect involving the ipsilateral mandibular Angle, type 3 had a bilateral defect involving neither side of the mandibular Angle, and type 4 had a bilateral defect involving the unilateral or bilateral mandibular Angle.Each type is further divided into type A (applicable) and type B (not applicable) according to whether the ipsilateral vessels are suitable for anastomosis. Type B requires anastomosis of the contralateral cervical vessels.For type 2 cases, it is necessary to indicate whether the condylar process is involved in order to decide which graft material to use: Unilateral condylar involvement is 2AC/BC, and no condylar involvement is 2A/B.Based on the above classification and considering the skin defect, the length of the mandibular defect, the need for dentures, and other special circumstances, the surgeon further determines the type of free bone flap to be used.
Preformed Reconstruction Plates are intended for use in oral and maxillofacial surgery, trauma and reconstructive surgery. This includes primary mandibular reconstruction, comminuted fractures and temporary bridging pending delayed secondary reconstruction, including fractures of edentulous and/or atrophic mandibles, as well as unstable fractures. Patient Benefit – through seeking to achieve satisfying aesthetic results and minimize operative time. Patient Specific Plates for Mandible eliminate induced mechanical stress from bending plates.
-
orthognathic 1.0 sagittal split fixed 4 holes p...
-
maxillofacial trauma micro T plate
-
maxillofacial reconstruction 120 ° L plate
-
locking maxillofacial micro straight bridge plate
-
flat titanium mesh-2D square hole
-
cranial snowflake interlink plate Ⅱ