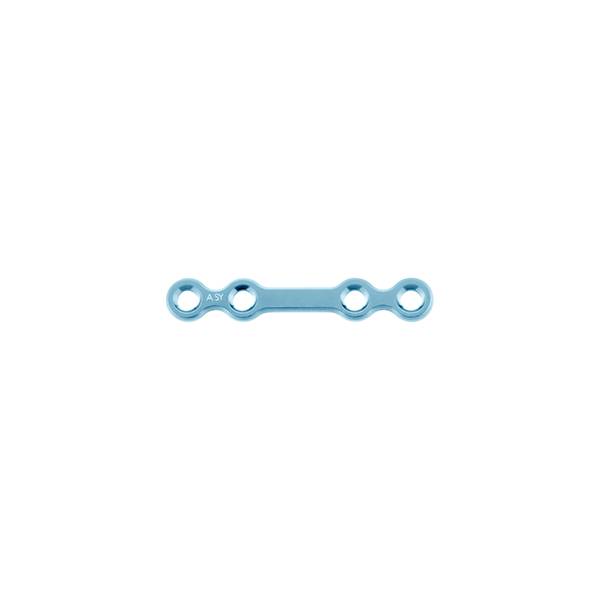
Material: medical pure titanium
Thickness: 0.8mm
Product specification
|
Item No. |
Specification |
|
|
10.01.09.04011023 |
4 holes |
23mm |
|
10.01.09.04011026 |
4 holes |
26mm |
|
10.01.09.04011029 |
4 holes |
29mm |
Features & Benefits:
• bone plate adopt special customized German ZAPP pure titanium as raw material, with good biocompatibility and more uniform grain size distribution.Don't affect MRI/CT examination.
• bone plate surface adopt anodizing technology, can enhance surface hardness and abrasive resistance.
Matching screw:
φ2.0mm self-drilling screw
φ2.0mm self-tapping screw
Matching instrument:
medical drill bit φ1.6*12*48mm
cross head screw driver: SW0.5*2.8*95mm
straight quick coupling handle
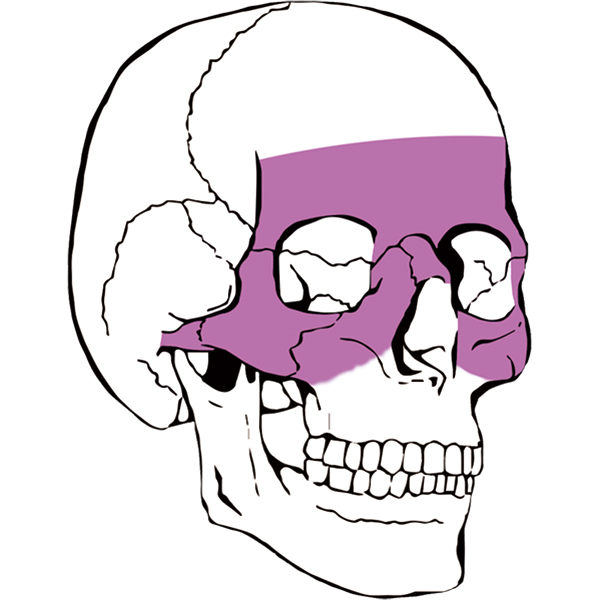
Maxillofacial trauma, also called facial trauma, it is any physical trauma that happen to the face. Maxillofacial trauma can been devided into soft tissue injuries, including burns, bruises and lacerations, or fractures of the facial bones such as eye injuries, nasal fractures and jaw fractures. fractures may lead to pain, swelling, function loss, shape changes of facial structures.
maxillofacial injuries may result in disfigurement and facial function loss; such as blindness or difficulty moving the jaw. There has low possibility to life-threatening, but maxillofacial trauma can also be deadly, because it can cause severe bleeding or interference with the airway; thus a primary concern in treatment is ensuring that the airway is open and not threatened so that the patient can breathe. When bone fractures are suspected, use radiography to diagnosis. It is necessary to perform treatment for other injuries such as traumatic brain injury, which commonly accompany severe facial trauma.
Just like other fractures, maxillofacial bone fractures exist with pain, bruising, and surrounding tissues swelling. Profuse nosebleeds may occur on the Fractures of the nose fracutre, maxilla fracture, and skull base fracture.Nasal fractures may be associated with deformity of the nose, as well as swelling and bruising. People with mandibular fractures often have pain and difficulty mouths opening and may have numbness in the lip and chin. In the case of Le Fort fractures, the midface may move relative to the rest of the face or skull.
Fracture of the maxilla fracture
1. Fracture line the maxillary bone is connected with the nasal bone, zygomatic bone and other craniofacial bones. Fracture line is prone to occur in sutures and weak bone walls.Le Fort classified the fracture into three types according to the height and height of the fracture line.
Type I fracture: also known as lower maxillary fracture or horizontal fracture.The fracture line extends horizontally from the piriform foramen to the maxillary pterygoid suture on both sides in the superior direction of the alveolar process.
Type II fracture is also called median maxillary fracture or conical fracture.The fracture line from the nasofrontal suture crossed the bridge of the nose, medial orbital wall, orbital floor and orbital maxillary suture laterally, and then followed the lateral wall of the maxilla to the pterygeal process.Sometimes can sweep the ethmoid sinus up to the anterior fossa, cerebrospinal fluid rhinorrhea.
Type III fracture is also called maxillary high level fracture or craniofacial separation fracture.Fracture line from the nose frontal suture to both sides across the bridge of the nose, orbit, through the zygomaticofrontal suture back to the pterygeal process, the formation of craniofacial separation, often lead to the middle of the face elongation and depression, this type of fracture accompanied by skull base fracture or craniocerebral injury, ear, nose bleeding or cerebrospinal fluid leakage.
2. Fracture segment displacement usually occurs posterior and inferior displacement.
3. Occlusal disorder.
4. Orbital and periorbital changes orbital and periorbital often accompanied by tissue bleeding, edema, the formation of a unique "eyeglass symptoms", often manifested as periorbital ecchymosis, upper and lower eyelid and bulbous conjunctival bleeding, or eye displacement and diplopia.
5. Brain injury.
Treatment methods for maxillofacial injuries include:
1. Maxillofacial soft tissue injury: the treatment principle is timely debridement, and the displaced tissue is restored and sutured.During debridement, the tissue should be preserved as far as possible to reduce the defect and the influence on the patient's facial shape after injury.
2, jaw fracture: fracture end reduction, using internal fixation method to fix the affected place, restore the continuity of the jaw, try to restore the normal preoperative occlusal relationship.
-
mastoid interlink plate
-
maxillofacial trauma micro X plate
-
locking maxillofacial micro double Y plate
-
orthodontic ligation nail 2.0 self drilling �...
-
maxillofacial trauma mini rectangle plate
-
drainage cranial interlink plate II