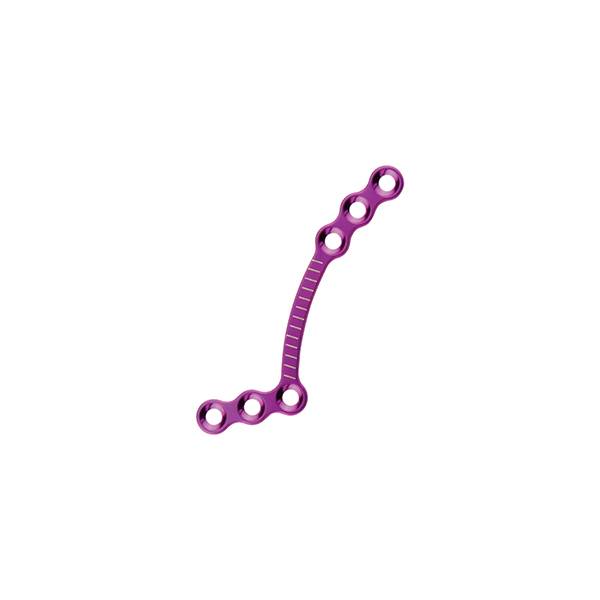
Material: medical pure titanium
Thickness: 0.6mm
Product specification
|
Item No. |
Specification |
||
|
10.01.07.06113004 |
left |
S |
18mm |
|
10.01.07.06213004 |
right |
S |
18mm |
|
10.01.07.06113008 |
left |
M |
20mm |
|
10.01.07.06213008 |
right |
M |
20mm |
|
10.01.07.06113012 |
left |
L |
22mm |
|
10.01.07.06213012 |
right |
L |
22mm |
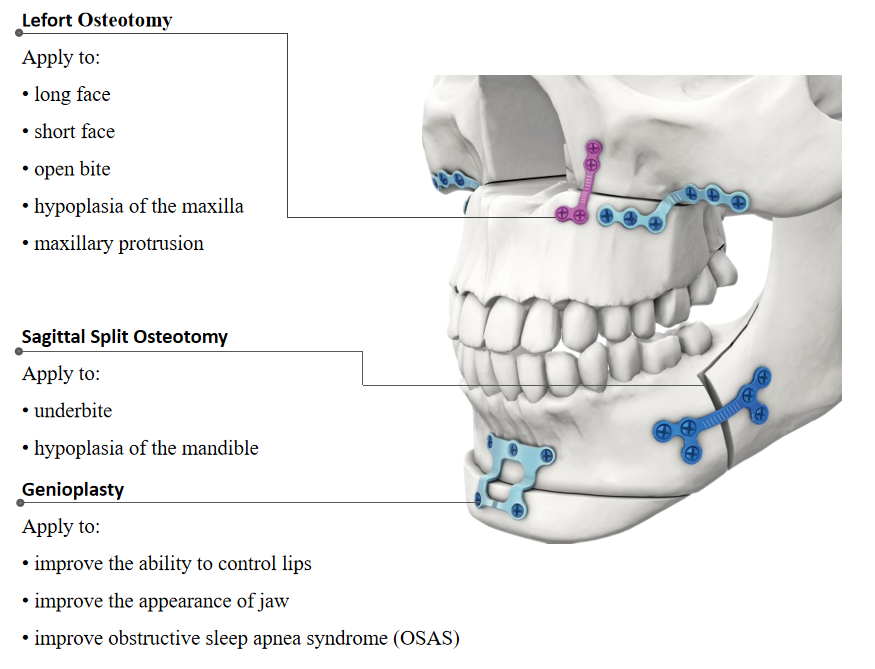
Application
Features & Benefits:
• connect rod part of plate has line etching in every 1mm, easy moulding.
• different product with different color, convenient for clinician operation
Matching screw:
φ1.5mm self-drilling screw
φ1.5mm self-tapping screw
Matching instrument:
medical drill bit φ1.1*8.5*48mm
cross head screw driver: SW0.5*2.8*95mm
straight quick coupling handle
Etched lines, in 1 mm increments, on implants provide a visual aid for plate bending.
Oral and maxillofacial deformity refers to the abnormal size and shape of the maxilla caused by the abnormal development of the maxilla, the abnormal relationship between the upper and lower maxilla and its relationship with other craniofacial bones, as well as the abnormal relationship between the maxilla and teeth, the abnormal function of the oral and maxillary system and the abnormal facial morphology.The purpose of orthognathic surgery is to correct the misplaced teeth, adjust the discordant dental arch and the relationship between teeth and jaws, eliminate the interference between teeth and jaws, arrange the dentition, and eliminate the compensatory inclination of teeth, so as to enable the operation to move the incised bone segment to the designed correction position smoothly, and establish a good relationship between teeth and jaws.
As early as 1928, Fauchard had tried to correct a single tooth dislocation with a dental clamp, but the surgical treatment of bony tooth and jaw deformities was developed by Hullihen in 1848 and first reported in 1849.Since then, although many scholars have made efforts to explore and improve, the treatment effect is not ideal due to the limited technology and medical level at that time, so that in the following 100 years, the treatment of dental and maxillofacial deformities progresses slowly.Until the late 1950s, with the development of anesthesiology, basic surgery, applied anatomy and special surgical instruments, the surgical correction of dental and maxillofacial deformities has developed rapidly.
In 1957, Trauner and Obwegeser reported for the first time that the sagittal split ramus osteotomy using the intraoral approach was improved by Dal Pony (1961), marking a new stage of surgical treatment of maxillofacial deformities.Since the 1970 s, because of the Bell and efforts of many scholars, in the jaw of jaw and tissue blood supply system of applied anatomy, and cut bone blood supply after the dynamic changes of a breakthrough, further laid the biological basis of modern are jaw surgery, in order to achieve each tooth - - sticky periosteal bone transplantation of composite tissue pedicle translocation, provides the scientific basis and guarantee of success.In addition, the establishment of the principle of surgical-orthodontic combined treatment makes the surgical treatment of dental and maxillofacial deformities more perfect, and truly enters a new period of combining function with morphology.
Because the surgical treatment of patients with dental and maxillofacial deformities should be based on the deformities and treatment requirements, the dental and bone complex should be cut open and moved to reconstruct the three-dimensional spatial relationship and function of the normal dental and maxillofacial structure, and to obtain satisfactory cosmetic effect of the maxillofacial.Therefore, the treatment plan, tooth?The adjustment of the relationship, the location of the bone incision, the direction and distance of the bone movement, and the choice of the surgical plan should all be accurately considered and designed before the operation, and the expected therapeutic effect of the selected plan should be predicted preoperatively.
Orthognathic surgery is used to solve the functional abnormalities or facial morphology abnormalities caused by the abnormal size and shape of the maxilla caused by the development of the maxilla, as well as the abnormal relationship between the size and shape of the maxilla and other facial bones.Surgery may be required to improve the facial features, including severe upper alveolar anterior protrusion (buckteeth), lower alveolar anterior protrusion (overbite), large anterior jaw openings, and severe bony deviations.